GLP-1s, or Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, are a class of medications commonly prescribed for individuals with type 2 diabetes. They work by mimicking the effects of the naturally occurring hormone GLP-1, which stimulates insulin release, reduces glucagon secretion, slows gastric emptying, and promotes satiety. While GLP-1s are effective in managing blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss, like any medication, they may come with certain side effects that patients should be aware of. Here, we’ll delve into some of the common side effects associated with GLP-1s:
- Nausea: One of the most frequently reported side effects of GLP-1s is nausea. This typically occurs when starting the medication or increasing the dosage and tends to improve over time as the body adjusts. Eating smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding fatty or rich foods may help alleviate nausea.
- Vomiting: In some cases, nausea may progress to vomiting, although this is less common. Patients experiencing persistent or severe vomiting should consult their healthcare provider, as it may indicate the need for a dosage adjustment or a switch to a different medication.
- Diarrhea: GLP-1s can also cause gastrointestinal disturbances, including diarrhea. Like nausea, this side effect often diminishes with continued use but may require management strategies such as staying hydrated and consuming a balanced diet with adequate fiber.
- Hypoglycemia: While GLP-1s primarily lower blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin release, they can occasionally lead to hypoglycemia, especially when combined with other diabetes medications like sulfonylureas or insulin. Patients should be educated on the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and instructed on appropriate management techniques.
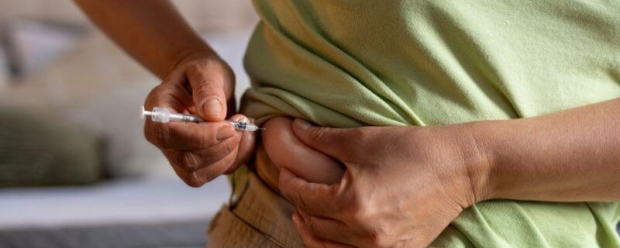
- Injection-site reactions: Since GLP-1s are administered via subcutaneous injection, some individuals may experience reactions at the injection site, such as redness, itching, or swelling. Rotating injection sites and proper injection technique can help minimize these effects.
- Pancreatitis: Although rare, GLP-1s have been associated with an increased risk of pancreatitis, a potentially serious inflammation of the pancreas. Patients should be advised to seek medical attention if they experience persistent abdominal pain, particularly if accompanied by nausea, vomiting, or fever.
- Weight loss: While weight loss is often a desired outcome of GLP-1 therapy, excessive or rapid weight loss may occur in some individuals. Healthcare providers should monitor patients’ weight regularly and adjust treatment as needed to prevent unintended outcomes.
It’s important for individuals prescribed GLP-1s to be aware of these potential side effects and to communicate openly with their healthcare providers about any concerns or symptoms they experience. While most side effects are mild and transient, prompt medical attention may be necessary in certain cases to ensure the safe and effective management of diabetes. As always, healthcare decisions should be made in collaboration with a qualified provider who can tailor treatment to each patient’s individual needs and circumstances.